Xenoestrogens: What Are They and Where Are They Found?

The endocrine system is a sophisticated collection of glands that secrete hormones to ensure our cells receive the right information to regulate a wide variety of functions. When the endocrine system is humming along nicely, we’re more likely to experience good health. The endocrine system is susceptible to many external forces that can send it out of balance and one of the strongest influencers is a class of chemicals called xenoestrogens. It’s important to know what xenoestrogens are, where they’re found and also, what we can do avoid them and reduce their effect on us.
It doesn’t take much to throw the entire endocrine system out of balance, and exposure to xenoestrogens, often measured in parts per billion, can literally be the straw that breaks the camel’s back, and be the tipping point for a cascade of hormonal imbalance.
What are Xenoestrogens?
Xenoestrogens are man-made chemicals that disrupt the endocrine system and meddle with our ability to excrete estrogen, potentially leading to estrogen dominance as well as developmental, reproductive, neurological and immune effects. To my knowledge, xenoestrogens never have the potential for positive action. They are only a risk.
What’s The Difference Between Xenoestrogens and Phytoestrogens?
Xenoestrogens are very different from phytoestrogens, which are compounds found in certain plant foods that mimic our own production of estrogen in the body. Phytoestrogens may have a positive effect or a negative effect depending on the individual and his or her health circumstances.
Where Are Xenoestrogens Found?
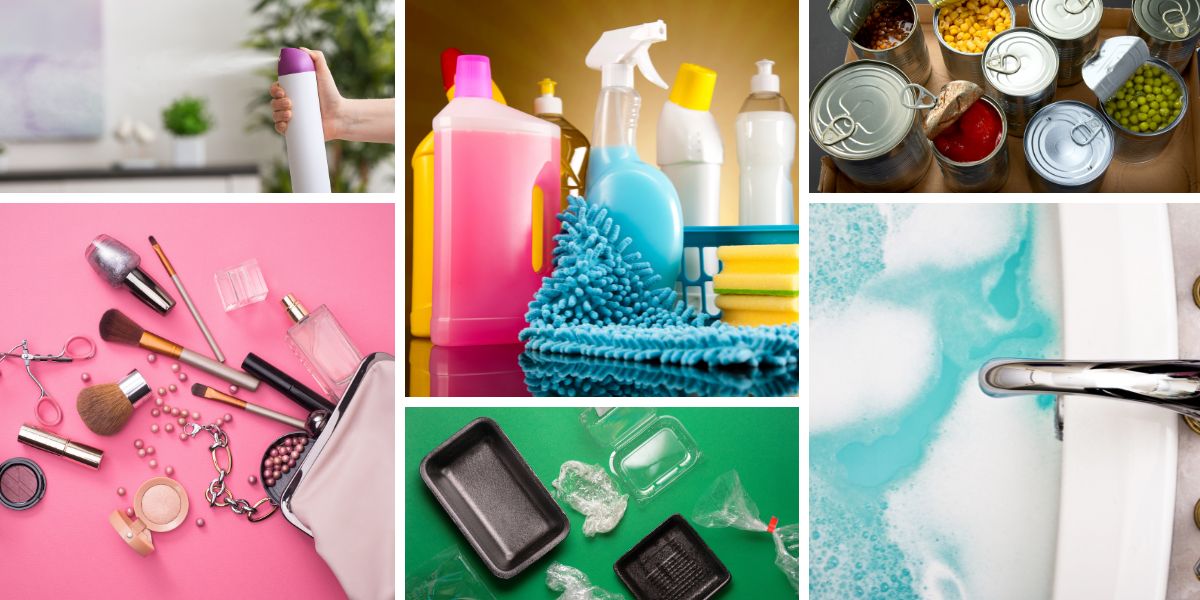
Hold on to your hats, because xenoestrogens are almost everywhere. Sources of xenoestrogens include:
- Water (tap water and bathing)
- Pesticides, herbicides and insecticides, including glyphosate as found in conventional food, and even tampons
- Cleaning products (home and industrial)
- Plastics (food, beverages, storage containers, non-food packaging and industrial plastics)
- Canned foods
- Dental sealants
- Receipts
- Air and dust
- Air fresheners
- Laundry products (detergent, fabric softener, dryer sheets, etc.)
- Hair dyes
- Nail polish and nail polish removers
- Cosmetics
- Personal care products (shampoo, conditioner, deodorant, moisturizer, body wash, etc.)
- Perfume
- Sunscreen
- Medical devices
- Birth control pills
- Toys
- Building materials
- Home furnishings (including furniture, carpets, window drapes, mattresses/foams, bedding)
- Photocopiers and printers
- Artificial food dyes
While this list may seem overwhelming, the good news is there are ways we can reduce our exposure in our own homes (more on that below).
If you’re interested in learning more about how we can reduce our exposure to xenoestrogens and other chemicals in the home, click here to check out my Healthy At Home course.
Health Risks of Xenoestrogens
The body naturally produces estrogen. This type of estrogen is called endogenous – or made by the body. We often start messing with its balance from a young age – with baby bottles, and toys (and now that slime craze), and top off our teens with some birth control pills. As you’ll note above, xenoestrogens are found in all forms of plastic.
Xenoestrogens mimic estrogen in the body and can out-compete the estrogen we make, leading to hormonal and endocrine disruption. Xenoestrogens can be up to 1,000 times more powerful than endogenous estrogens. The greater our exposure, the greater the impact. They are extremely powerful and are stored in our fat cells. In the last 50 years, researchers have noticed an increase in the incidence of diseases associated with these endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
Some of the health risks of xenoestrogens include:
Cancer
- Endocrine disruptors are connected to hormone-dependent cancers like breast cancer and prostate cancer
- Prostate cancer incidence has nearly tripled from 1975 to 2007
- Breast cancer incidence in women has increased by 57% from 1977 to 2007
- Xenoestrogens are linked to other cancers including pancreatic, lung, kidney, brain and testicular
Infertility
- Xenoestrogens can cause infertility in couples and lower sperm count in men
- Can influence endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease and PCOs in women
- Can even be linked to the decline of sex ratios (male to female births)
Obesity
- Xenoestrogens accumulate in fat tissue
- This can lead to the accumulation of excess fatty tissues in the body, altered metabolism, increased appetite and obesity
Diabetes
- Exposure to organochlorine pesticides, phthalates and PCBs are linked with insulin resistance and risk of developing Type 2 diabetes
Thyroid Disruption
How to Reduce Xenoestrogen Exposure
You can mitigate the effects of xenoestrogens in a variety of simple and straightforward ways. Yes, there are some sources of xenoestrogens that we cannot control, but overall there are many ways that we can reduce our exposure, as well as rid of xenoestrogens from our bodies.
Evidence indicates that in adults, the effects can be improved or reversed when we remove xenoestrogens from our lives. Unfortunately, fetuses, infants and children are more susceptible to the effects of xenoestrogens and the damage can be permanent. (For more on creating an optimal environment for babies and children, check out my posts on preconception planning, breastfeeding, baby food introductions and healthy nursery essentials.)
While this list of ways to reduce xenoestrogen exposure may seem long or overwhelming, each tip in and of itself isn’t excruciating or onerous, plus I provide plenty of additional links to help you. Prioritize and pick what makes the most sense for you to start with. You could begin with the xenoestrogen sources you use the most (like personal care products or cleaning products, for example), or decide based on what suits your budget.
15 Ways to Reduce Xenoestrogen Exposure
1. Buy or Make Natural Beauty Care Products
Why Do It: The average woman uses 12 products with 168 chemical ingredients daily, while men use 6 products that contain about 85 ingredients. Altogether, 12.2 million adults are exposed to ingredients that are considered known carcinogens every single day because of their personal care products. The common ingredients in lotions and potions are considered safe in small amounts. But all those little small amounts add up.
How to Do It: 20 Best Natural Beauty Care Recipes and 13 Ingredients to Avoid In Personal Care Products
2. Switch to Natural Deodorant
Why Do It: Conventional deodorants and antiperspirants contain ingredients that are linked to allergic reactions, skin conditions, neurological issues and cancer.
How to Do It: How to Choose a Good Natural Deodorant
3. Skip Synthetic Perfumes
Why Do It: The chemicals in perfumes are associated with endocrine disruption, respiratory issues, asthma, dermatitis and headaches.
How to Do It: Is Your Perfume Poisoning Your Family?
4. Use Natural Cleaning Products
Why Do It: Conventional cleaning products contain a cocktail of chemicals that are worse for us than the dirt itself. Many have volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that are known carcinogens, plus cleaning products are connected with allergies, respiratory issues, hormone disruption, eczema, asthma and cancer. The chemicals in cleaning products linger in the air long after we clean and while they are stored.
How to Do It: The Ultimate Guide to Non-Toxic Home Cleaning, 10 Non-Toxic Home Cleaning Recipes and 5 Essential Oils to Clean Your Home
5. Get a Water Filter
Why Do It: Tap water is treated with chemicals that disrupt endocrine function and digestive health, and it can be contaminated with drugs, conventional beauty care products or cleaning products that people are using.
How to Do It: How to Choose a Water Filter
6. Install a Shower Filter
Why Do It: Most water sources are treated with chlorine and evidence indicates that showering in chlorinated water might actually be worse than drinking it. Combined with the heat of showers, chlorine and chlorine byproducts are absorbed through our skin and inhaling them through our lungs.
How to Do It: Is Your Shower Harming Your Health?
7. Ditch the Non-Stick Pans
Why Do It: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PFTE) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), the main chemicals in Teflon cookware, are carcinogenic, can cause flu-like symptoms and can even be found in human breastmilk. These chemicals leach into our food as we cook and then we consume them.
How to Do It: Your Guide to Healthy Cookware Options
8. Store Food Without Plastic
Why Do It: Plastics threaten our endocrine systems and hormonal health, the environment, our oceans and marine life. One of the main chemicals in plastics is bisphenol A (BPA), a known endocrine disruptor. This led companies to make products that were BPA-free; unfortunately, the evidence is showing that these BPA-free alternatives can be just as damaging.
How to Do It: 5 Ways to Store Food Without Plastic and How to Stop Using Aluminum Foil, Plastic Wrap and Other Kitchen Disposables
9. Choose Organic Produce and Other Food
Why Do It: Chemically grown food is loaded with xenoestrogenic pesticides, insecticides and herbicides that affect hormone health and increase the risk of cancer. Studies show that organic produce has more anti-oxidants (which help to fight damage to our bodies) and lower pesticide residues, and can help reduce cancer risk.
How to Do It: Check out What’s On My Food?, an index of the pesticides in produce. If budgeting is a factor, use the Environmental Working Group’s Guide to Pesticides in Produce, which outlines the foods with the most and least pesticide residues. These 10 Questions to Ask Your Farmer at the Market are also helpful!
10. Poop Regularly
Why Do It: Effective and daily elimination allows us to excrete any harmful or damaging wastes, including excess estrogen.
How to Do It: Ways to Reduce Constipation
11. Say No To Receipts
Why Do It: Thermal paper receipts are contain BPA, which disrupts our hormones and can lead to cancer.
How to Do It: Say ‘no thank you’ to receipts you won’t need. Some stores offer electronic receipts, or you can shop online where receipts are sent via email.
12. Purchase Air Filtering Plants
Why Do It: A variety of factors affect indoor air, including dust, outdoor air pollution, chemicals in cleaning products and air fresheners, mold, or cigarette smoke. Plants are an easy way to help filter the air!
How to Do It: Plants such as ficus, aloe, spider plant and Boston fern can help with air filtration.
13. Replace Your Bedding
Why Do It: Conventional cotton is heavily sprayed with pesticides that can disrupt hormones and lead to cancer. These chemicals stay in our sheets, where we inhale them as we sleep, but they also spread throughout our homes and when we wash them, they have the potential to react with the chemicals in the municipal water to create harmful byproducts.
How to Do It: Natural Bedding and Linens Guide
14. Use an Infrared Sauna
Why Do It: We are able to release a number of toxins through sweating, including BPA, as well as heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, cadmium and mercury.
How to Do It: Health Benefits of Infrared Saunas
15. Swap Tampons and Pads for Better Alternatives
Why Do It: The average woman menstruating for five days a month for 38 years will use approximately 11,400 tampons in a lifetime, with direct contact to the chemicals in tampons for 2,200 days. One of the chemicals found in tampons and pads is dioxin, which interferes with our hormones.
How to Do It: Natural Alternatives to Tampons
You don’t have to do every single one of these things at once. Even if you only pick a couple of things on this list to start, you’re still going to be improving your health and you can always do more in the future.

Free Resource Library
Enjoy more than 40 downloadable guides, recipes, and resources.